|
hc8meifmdc|20005939267D|healthm_live|health_library|health_library_details|0xfdff558d090000005a02000001000700
| Overview |
|
Tocotrienols are part of the vitamin E family. The Vitamin E family is comprised of eight different compounds: alpha, beta, gamma and delta-tocotrienols and tocopherols. Tocopherols are the most common form used for vitamin E fortification, but tocotrienols may be a more potent source of vitamin E. Tocotrienols have similar structure to tocopherols but contain three double bonds in the carbon side chain of the molecule. This unique structure makes tocotrienols a potent anti-oxidant with many health benefits. Tocotrienols are found in numerous sources in nature, with oil extracted from palm fruit being the source with the highest tocotrienol content.
What is Tocotrienols ?
Vitamin E is one of the most important phytonutrients in edible oils. It consists of eight naturally occuring isomers, a family of four tocopherols (alpha, beta, gamma and delta) and four tocotrienols (alpha, beta, gamma and delta) homologues.
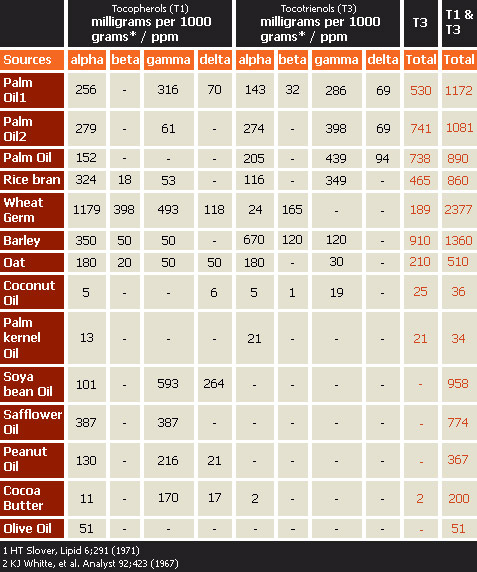
Where it is found
Edible oil originating from plants are rich source for tocotrienols. Crude palm oil extracted from the fruits of oil palm Elaeis guineensis particularly contains a high amount of tocotrienols (up to 800 mg/kg), mainly consisting of gamma-tocotrienol, alpha-tocotrienol and delta-tocotrienol.
|
| |
 |
|
|
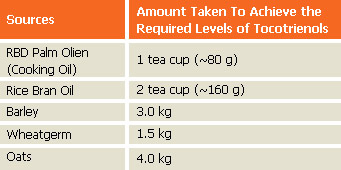
Tocotrienols From Normal Diet Alone
Since tocotrienols only occur at very low levels in nature, with the highest concentration found in palm oil, it is virtually impossible to attain the amount of tocotrienols that show beneficial effects from the normal diet alone. For example, one would need to consume a cup of palm olein (cooking oil) a day to get the level required for effectiveness as described in most studies. |
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
Benefits / uses
Cholesterol Reduction
Inhibit cholesterol production in the liver, thereby lowering total blood cholesterol. Alpha tocotrienol suppresses hepatic HMG-CoA reductase activity that results in the lowering of LDL cholesterol levels.
Tocotrienols which are naturally occurring in palm oil, have been shown to suppress / lower plasma cholesterol in human. Combination of gamma-tocotrienol and alpha-tocopherol is found as a potential hypolipemic agent in hyperlipemic humans at atherogenic risk. Tocotrienols inhibit cholesterogenesis by suppressing HMG-CoA reductase.
Reversing Carotid Atherosclerosis
Reverses arterial blockage (carotid atherosclerosis), hence reducing the risk factors for cardio-vascular diseases such as atherosclerosis and stroke. Palm based tocotrienol is the first and natural compound to be shown by human study to have the ability to reverse atherosclerosis. Medical human research showed that patients with confirmed carotid atherosclerosis, who consumed 240mg of palm based tocotrienol complex per day for 18-36 months had a decrease in the amount of cholesterol plaque in their carotid artery while those receiving placebo did not show such an effect. Palm based tocotrienol complex protects the ApoE knockout mice against cholesterol build-up and hence prevent arteriosclerosis.
Protection Against Ischemia/Reperfusion Heart Injury.
Medical study suggests that palm based tocotrienols were more efficient than alpha-tocopherol alone in the protection of the heart against oxidative stress induced by ischemic reperfusion.
Inhibit of Platelet Aggregation
Delta-tocotrienol was significantly more potent than the alpha and gamma-tocotrienols, in the inhibition of platelet aggregation. Palm based tocotrienols may serve as an antithrombotic agent by decreasing platelet aggregation significantly
Most Cardioprotective
Based on new scientific publication on tocotrienol and cardioprotection - gamma-tocotrienol is the most potent for cardioprotection.
Neuroprotection
Based on on-going NIH-funded study and in collaboration with the Ohio State University Medical Center - Prof. Chandan Sen has published 5 peer-reviewed papers which proved that alpha-tocotrienol is the most potent in preventing stroke-induced injuries to the brain.
Anti-cancer and Tumour Suppresive
Palm based tocotrienols had shown to inhibit human breast cancer cells irrespective of estrogen receptor status. Tocopherol has no effect at all on human breast cancer cells. Delta - tocotrienol was found to be the most effective tocotrienols in inducing apoptosis (cell death) in estrogen-responsive and estrogen-nonresponsive human breast cancer cells. Confer anti-cancer properties. Inhibit tumor growth of certain cancers. Alpha-tocotrienol and gamma-tocotrienol have shown to prolong the life span of cancer-infected mice. Gamma-tocotrienol is 3 times more potent in inhibiting growth of human breast cancer cultured cells than Tamoxifen. Published research from the East Tennessee University and MD Anderson Cancer Center (Texas) revealed that gamma-tocotrienol was the most potent in inhibiting prostate cancer cells.
Potent Natural Super - Antioxidant
Alpha-tocotrienol has been shown to be 40 - 60 times more potent than alpha-tocopherol as an antioxidant in the prevention of lipid peroxidation. Effective antioxidant in the prevention of protein oxidation and lipid peroxidation after strenous exercise for athletes, joggers and body builders.
Anti - Aging / Cosmetics and Personal Care
Preferentially accumulates at the stratum corneum of the skin. First line of defense against free radicals generated in the skin by UV/ozone rays. Prevention of skin aging and damage by oxidative rays. Being a more potent antioxidant, the tocotrienols neutralizes free radicals at a faster rate and hence protect tocopherols. Protection against UV-induced skin damage and skin aging. Tocotrienols topically applied onto the skin was found to penetrate rapidly through the skin and the highest concentrations are found in the uppermost 5 microns. Tocotrienol-treated skin contained Vitamin E at concentration 7-30 fold higher than control values. Tocotrienol augments the efficacy of sunscreens containing compounds that reduce penetration of or absorb ultraviolet radiation.
Lower Blood Pressure
Palm gamma-tocotrienol has ability to prevent development of increased blood pressure in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats (SHR) after 3 months supplementation.
Research studies / References
|
 |
Sen CK, Khanna S, Roy S (2007). "Tocotrienols in health and disease: the other half of the natural vitamin E family". Molecular Aspects of Medicine 28 (5-6): 692-728. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2007.03.001. PMC 2435257. PMID 17507086. |
|
|
 |
Kamal-Eldin A, Appelqvist LA (July 1996). "The chemistry and antioxidant properties of tocopherols and tocotrienols". Lipids 31 (7): 671-701. doi:10.1007/BF02522884. PMID 8827691. |
|
|
 |
Clarke MW, Burnett JR, Croft KD (2008). "Vitamin E in human health and disease". Critical Reviews in Clinical Laboratory Sciences 45 (5): 417-50. doi:10.1080/10408360802118625. PMID 18712629. |
|
|
 |
Dunphy, P. J.; Whittle, K. J.; Pennock, J. F.; Morton, R. A. (1965). "Identification and Estimation of Tocotrienols in Hevea Latex". Nature 207 (4996): 521. doi:10.1038/207521a0. |
|
|
 |
Tocotrienols: Vitamin E Beyond Tocopherols By Ronald R. Watson, Victor R. Preedy, 2008 |
|
|
 |
Tan, B. and M.H. Saleh, Integrated process for recovery of carotenoids and tocotrienols from oil in USPTO 5,157,132. 1992 |
|
|
 |
Packer L, Weber SU, Rimbach G (February 2001). "Molecular aspects of alpha-tocotrienol antioxidant action and cell signalling". The Journal of Nutrition 131 (2): 369S-73S. PMID 11160563. http://jn.nutrition.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=11160563. |
|
|
 |
Pruthi S, Allison TG, Hensrud DD (November 2001). "Vitamin E supplementation in the prevention of coronary heart disease". Mayo Clinic Proceedings 76 (11): 1131-6. doi:10.4065/76.11.1131. PMID 11702901. |
|
|
 |
Inokuchi H, Hirokane H, Tsuzuki T, Nakagawa K, Igarashi M, Miyazawa T (July 2003). "Anti-angiogenic activity of tocotrienol". Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry 67 (7): 1623-7. doi:10.1271/bbb.67.1623. PMID 12913317. |
|
|
 |
Theriault A, Chao JT, Wang Q, Gapor A, Adeli K (July 1999). "Tocotrienol: a review of its therapeutic potential". Clinical Biochemistry 32 (5): 309-19. doi:10.1016/S0009-9120(99)00027-2. PMID 10480444. |
|
|
 |
Pearce BC, Parker RA, Deason ME, Qureshi AA, Wright JJ (October 1992). "Hypocholesterolemic activity of synthetic and natural tocotrienols". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 35 (20): 3595-606. doi:10.1021/jm00098a002. PMID 1433170. |
|
|
 |
a b "Oral toxicity of a tocotrienol preparation in rats". Food and chemical toxicology 39 (8): 299-805. 2001. PMID 11434987. Archived on 2009-12-23. Error: If you specify |archiveurl=, you must first specify |url=. http://www.webcitation.org/5mF7XYaTU. Retrieved 2009-12-23. |
|
|
 |
Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs): Recommended Intakes for Individuals, Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine, National Academies, 2004, http://www.iom.edu/Global/News%20Announcements/'/media/Files/Activity%20Files/Nutrition/DRIs/DRISummaryListing2.ashx, retrieved 2009-06-09 |
|
|
 |
Khanna S, Roy S, Slivka A, et al. (October 2005). "Neuroprotective properties of the natural vitamin E alpha-tocotrienol". Stroke 36 (10): 2258-64. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000181082.70763.22. PMC 1829173. PMID 16166580. |
|
|
 |
Sen CK, Khanna S, Roy S, Packer L (April 2000). "Molecular basis of vitamin E action. Tocotrienol potently inhibits glutamate-induced pp60(c-Src) kinase activation and death of HT4 neuronal cells". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 275 (17): 13049-55. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.17.13049. PMID 10777609. |
|
|
 |
Khosla P, Patel V, Whinter JM, et al. (2006). "Postprandial levels of the natural vitamin E tocotrienol in human circulation". Antioxidants & Redox Signaling 8 (5-6): 1059-68. doi:10.1089/ars.2006.8.1059. PMID 16771695. |
|
|
 |
Klapman J, Malafa MP (October 2008). "Early detection of pancreatic cancer: why, who, and how to screen". Cancer Control 15 (4): 280-7. PMID 18813195. http://www.moffitt.org/CCJRoot/v15n4/pdf/280.pdf. |
|
|
 |
Malafa MP (October 2008). "New insights and gains in pancreatic cancer". Cancer Control 15 (4): 276-7. PMID 18813194. http://www.moffitt.org/CCJRoot/v15n4/pdf/276.pdf. |
|
|
 |
Kamat JP, Devasagayam TP (August 1995). "Tocotrienols from palm oil as potent inhibitors of lipid peroxidation and protein oxidation in rat brain mitochondria". Neuroscience Letters 195 (3): 179-82. doi:10.1016/0304-3940(95)11812-B. PMID 8584204. |
|
|
 |
Kamat JP, Sarma HD, Devasagayam TP, Nesaretnam K, Basiron Y (May 1997). "Tocotrienols from palm oil as effective inhibitors of protein oxidation and lipid peroxidation in rat liver microsomes". Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry 170 (1-2): 131-7. doi:10.1023/A:1006853419214. PMID 9144327. |
|
|
 |
Weng-Yew W, Selvaduray KR, Ming CH, Nesaretnam K (2009). "Suppression of tumor growth by palm tocotrienols via the attenuation of angiogenesis". Nutrition and Cancer 61 (3): 367-73. doi:10.1080/01635580802582736. PMID 19373610. |
|
|
 |
Chin SF, Hamid NA, Latiff AA, et al. (January 2008). "Reduction of DNA damage in older healthy adults by Tri E Tocotrienol supplementation". Nutrition 24 (1): 1-10. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2007.08.006. PMID 17884341. |
|
|
 |
Rahmat A, Ngah WZ, Shamaan NA, Gapor A, Abdul Kadir K (1993). "Long-term administration of tocotrienols and tumor-marker enzyme activities during hepatocarcinogenesis in rats". Nutrition 9 (3): 229-32. PMID 8102564. |
|
|
 |
Hussein D, Mo H (May 2009). "d-Dlta-tocotrienol-mediated suppression of the proliferation of human PANC-1, MIA PaCa-2, and BxPC-3 pancreatic carcinoma cells". Pancreas 38 (4): e124-36. doi:10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181a20f9c. PMID 19346993.
http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00985777 |
|
|
 |
Nesaretnam K, Guthrie N, Chambers AF, Carroll KK (December 1995). "Effect of tocotrienols on the growth of a human breast cancer cell line in culture". Lipids 30 (12): 1139-43. doi:10.1007/BF02536615. PMID 8614304. |
|
|
 |
Nesaretnam K, Stephen R, Dils R, Darbre P (May 1998). "Tocotrienols inhibit the growth of human breast cancer cells irrespective of estrogen receptor status". Lipids 33 (5): 461-9. doi:10.1007/s11745-998-0229-3. PMID 9625593. |
|
|
 |
Guthrie N, Gapor A, Chambers AF, Carroll KK (March 1997). "Inhibition of proliferation of estrogen receptor-negative MDA-MB-435 and -positive MCF-7 human breast cancer cells by palm oil tocotrienols and tamoxifen, alone and in combination". The Journal of Nutrition 127 (3): 544S-548S. PMID 9082043. |
|
|
 |
http://jn.nutrition.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=9082043. |
|
|
 |
Yu W, Simmons-Menchaca M, Gapor A, Sanders BG, Kline K (1999). "Induction of apoptosis in human breast cancer cells by tocopherols and tocotrienols". Nutrition and Cancer 33 (1): 26-32. doi:10.1080/01635589909514744. PMID 10227040. |
|
|
 |
Sylvester, Paul W.; Shah, Sumit (2002). "Antioxidants in Dietary Oils: Their Potential Role in Breast Cancer Prevention". Malaysian Journal of Nutrition 8 (1): 1-11. ISSN 1394-035X. http://myais.fsktm.um.edu.my/2687/.[unreliable medical source?] |
|
|
 |
Nesaretnam K, Ambra R, Selvaduray KR, Radhakrishnan A, Canali R, Virgili F (December 2004). "Tocotrienol-rich fraction from palm oil and gene expression in human breast cancer cells". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1031: 143-57. doi:10.1196/annals.1331.014. PMID 15753141. |
|
|
 |
Yap WN, Zaiden N, Tan YL, Ngoh CP, Zhang XW, Wong YC, Ling MT, Yap YL. (November 2009). "Id1, inhibitor of differentiation, is a key protein mediating anti-tumor responses of gamma-tocotrienol in breast cancer cells". Cancer Lett 291 (2): 187-99. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2009.10.012. PMID 19926394. | |
| |
|