|
hc8meifmdc|20005939267D|healthm_live|health_library|health_library_details|0xfdffb5ff8d0000008401000001000100
| Overview |
|
Diindolylmethane is formed in the body from plant substances contained in "cruciferous" vegetables such as cabbage, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, and broccoli. Scientists think these vegetables may help to protect the body against cancer because they contain diindolylmethane and a related chemical called indole-3-carbinol. |
 |
|
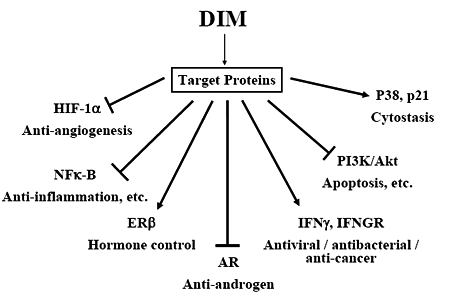
Diindolylmethane is used for preventing breast, uterine, and colorectal cancer. It is also used to prevent an enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hypertrophy, BPH) and treat premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
Diindolylmethane might act like estrogen in the body, but there is evidence that under certain circumstances it might also block estrogen effects.
|
| |
|
What is DIM?
Diindolylmethane, or DIM, is a compound that is formed in your body during the digestion of foods that contain the nutrient indole-3-carbinol. Indole-3-carbinol is found in cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower and Brussels sprouts. Eating these foods, therefore, provides your body with DIM. Diindolylmethane is also sold in supplemental form and is thought to provide a variety of health-promoting benefits.
Where it is found?
Good natural sources include broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, and cauliflower.
Benefits / uses
Estrogen Metabolism
Taking Diindolylmethane supplements increases the efficiency of the metabolic processing of estrogen. This increase in efficiency has been linked to increased antioxidant protection of the heart and brain. This process is also responsible for other benefits, such as an increase in libido in men and women and a decrease in moodiness for women.
Hormonal Balance
The increase in estrogen metabolism stimulates other hormones such as testosterone. This helps the body to return to a state of hormonal balance and optimal levels. When the body is at this level, it becomes more responsive to exercise and will increase its fat-burning metabolism, build lean muscle faster and promote an overall healthier body.
Preventative Medicine
Diindolylmethane is also used in a variety of roles in preventative medicine. It is believed that DIM helps to prevent certain cancers, including breast, colon and uterine cancers. It has also been linked to aiding with the prevention of enlarged prostates.
Treatments
The Diindolylmethane supplement is also used in treatments for common problems. Doctors may prescribe DIM to help with chronic breast pain, premenstual syndrome and endomitriosis.
Risk Reduction
Diindolylmethane has also been found to reduce the risks associated with hormone replacement therapy. Its positive affect on estrogen metabolism also makes DIM a common choice for reducing the effects of environmental estrogen exposure.
Doses
The appropriate dose of diindolylmethane depends on several factors such as the user's age, health, and several other conditions.
|
| |
|
Possible Side effects / Precautions / Possible Interactions:
Diindolylmethane is safe when consumed in the small amounts found in foods. There isn't enough information to know if supplements that contain larger amounts of diindolylmethane are safe.
Special Precautions & Warnings:
Pregnancy and breast-feeding: Diindolylmethane is safe when consumed in the small amounts found in foods. But don’t take larger amounts. Not enough is known about the safety of larger amounts during pregnancy and breast-feeding.
Hormone-sensitive conditions such as breast cancer, uterine cancer, ovarian cancer, endometriosis, or uterine fibroids: Diindolylmethane might act like estrogen, so there is some concern that it might make hormone-sensitive conditions worse. These conditions include breast, uterine, and ovarian cancer; endometriosis; and uterine fibroids. However, developing research also suggests that diindolylmethane might work against estrogen and could possibly be protective against hormone-dependent cancers. But stay on the safe side. Until more is known, don’t use diindolylmethane if you have a hormone-sensitive condition.
Reference & Research: |
 |
Rakel D.. Integrative Medicine. |
 |
Gong Y. Sohn H. Xue L. Firestone GL. Bjeldanes LF (2006). "3,3'-Diindolylmethane is a novel mitochondrial H(+)-ATP synthase inhibitor that can induce p21(Cip1/Waf1) expression by induction of oxidative stress in human breast cancer cells". Cancer Research 66 (9): 4880–4887. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4162. PMID 16651444. |
 |
Acharya A. Das I. Singh S. Saha T. (2010). "Chemopreventive properties of indole-3-carbinol, diindolylmethane and other constituents of cardamom against carcinogenesis". Recent patents on food, nutrition & agriculture 2 (2): 166–177. doi:10.2174/1876142911002020166. |
 |
Rogan EG (2006). "The natural chemopreventive compound indole-3-carbinol: state of the science". In Vivo 20 (2): 221–228. PMID 16634522. |
 |
Kim YS. Milner JA (2005). "Targets for indole-3-carbinol in cancer prevention". Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry 16 (2): 65–73. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2004.10.007. PMID 15681163. | |
| |
|