|
hc8meifmdc|20005939267D|healthm_live|health_library|health_library_details|0xfdff65bd010000001101000001002300
| Overview |
Alpha-GPC is a chemical released when a fatty acid found in soy and other plants breaks down. In Europe alpha-GPC is a prescription medication for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. It is available in two forms; one is taken by mouth, and the other is given as a shot. In the United States alpha-GPC is only available as a dietary supplement, mostly in products promoted to improve memory. Other uses for alpha-GPC include treatment of various kinds of dementia, stroke, and "mini-stroke" (transient ischemic attack, TIA). Alpha-GPC is also used for improving memory, thinking skills, and learning. Alpha-GPC seems to increase a chemical in the brain called acetylcholine. This brain chemical is important for memory and learning functions:
1. Increases human Growth Hormone (hGH)
Increases in endogenous human Growth Hormone (hGH) secretion by the anterior pituitary in conjunction with Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone (GHRH); that is, both Alpha-GPC and GHRH act concertedly to stimulate the release of hGH, naturally;
2. Improved mental focus and stimulation of cognitive function
Stimulation of the enzymatic synthesis of phosphatidylcholine (PC) in nerves, muscle cells and all cell membranes, counteracting the age-related decrease in phospholipid (PC) biosynthesis; thus, Alpha-GPC contributes directly to improved mental focus and stimulation of cognitive function;
3. More strength from work-outs and training programs
Acts as a precursor of acetylcholine (ACh); thus, Alpha-GPC activates cholinergic transmission which permits the development of more strength from work-outs and training programs, plus reducing levels of somatostatin in the hypothalamic-pituitary axis;
4. Improved lipotrophic functions in the liver
Elevations in blood and tissue levels of the essential nutrient, choline, which supports improved lipotrophic functions (methyl group transferases) in the liver. Research has shown that fatty liver, a condition associated with obesity, diabetes and heavy alcohol consumption, often leads to cirrhosis of the liver or liver failure. Studies conducted by Alan L. Buchman, M.D., associate professor of medicine at The Feinberg School of Medicine at Northwestern University, have shown that fatty liver can be prevented and possibly even eliminated with increased levels of choline. Alpha-GPC also acts synergistically with the body's store (and/or supplementation) of S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM or SAMe) and folic acid, vitamin B12 and vitamin B6 to facilitate methyl group transfers in the brain and liver;
5. Improved balanced and coordination
Produces improved balanced and coordination when combined with 'skill set' practice and training as a result of normalized nerve transmission in the brain, and in cardiac, skeletal and smooth muscles.
|
| |
| What is Alpha GPC? |
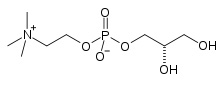 |
| [(2S)-2,3-dihydroxypropyl] 2-trimethylazaniumylethyl phosphate |
|
|
|
Alpha-GPC has been shown to potentiate the effects of growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) and increase human growth hormone (hGH) secretion in young and elderly individuals plus patients with Senile Dementia of the Alzheimer's Type (SDAT). Alpha-GPC also affects numerous biochemical and neurotransmitter systems that have been implicated in the development of age-related memory dysfunction (ARMD).
It is also a parasympathomimetic acetylcholine precursor which may have potential for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and is used as a nootropic dietary supplement to enhance memory and cognition. Alpha GPC rapidly delivers choline to the brain across the blood-brain barrier and is a biosynthetic precursor of the acetylcholine neurotransmitter. Alpha GPC is derived from highly purified soy lecithin.
|
| |
| Where it is Found? |
| L-Alpha Glycerylphosphorylcholine (Alpha GPC, choline alfoscerate) is a natural choline compound found in the brain and in milk. |
| |
|
|
|
| Benefits / Uses |
|
|
| |
Dosage
Commonly used doses are 300-1,200 mg daily.
Possible Side effects / Precautions / Possible Interactions
Alpha-GPC seems to be safe when used appropriately. It can cause side effects in some people including heartburn, headache, insomnia, dizziness, skin rash, and confusion.
Special Precautions & Warnings:
Pregnancy and breast-feeding: Not enough is known about the use of alpha-GPC during pregnancy and breast-feeding. Stay on the safe side and avoid use.
Interactions:
Scopolamine (Transderm Scop) interacts with ALPHA-GPC. Alpha-GPC increases a chemical in the brain called acetylcholine. Scopolamine blocks this same chemical. But it's not known if alpha-GPC decreases the benefits of scopolamine.
Research Studies / References
Administration of Alpha-GPC has been shown to improve neuropsychological parameters in patients with SDAT and ARMD. Alpha-GPC also improves memory and cognitive performance in patients with dementia, and benefits those recovering from cerebral ischemic attacks. Alpha-GPC has been shown to reduce the recovery time in comatose patients suffering from head injury and antagonize the effects of scopolamine to improve memory, attention, and performance in healthy individuals. Alpha-GPC's cognitive and growth hormone (GH) enhancing effects appear to be primarily the result of stimulation of the cholinergic neurotransmitter system; however, other biochemically-related modulations and neurotransmitter systems have been implicated.
Ageing, chronic or severe disease states, and prolonged stress - including athletic endeavors like marathons or 'ironman/ironwoman' events are associated with decreased hormone production, especially reduced secretion of human Growth Hormone (hGH) from the anterior pituitary. These life events are also associated with lower levels of free choline in the blood and tissues. Concomitantly, both quality of life and lifespan decrease, sexual desire and potency diminish, resistance to disease is reduced, muscles loose both protein (mass) and tone, and body fat levels increase.
In clinical situations, significantly reduced secretion of hGH is associated with short stature, generalized muscle wasting, Andropause, anxiety, undesirable mood and affect changes which are often associated with depression, abnormal sleep patterns, loss of energy and stamina, and decreased cellular and humoral (antibody) immune functions leading to increased susceptibility to disease. Since 1984, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the use of recombinant human Growth Hormone (hGH) for the treatment of dwarfism due to hGH deficiency, Adult Onset Growth Hormone Deficiency (Somatopause), Turner's syndrome, and wasting associated with AIDS/HIV. Alpha-GPC can be used in anti-aging programs, as a less expensive alternative to injecting recombinant hGH, and to treat or reduce the symptoms of the Somatopause.
Fate and distribution studies demonstrate that orally administered Alpha-GPC is absorbed quickly from the gastrointestinal tract and is transported in the blood to all cells and tissues, especially the brain. Alpha-GPC crosses the 'blood-brain' barrier and acts as a central nervous system (CNS) cholinergic stimulant while it simultaneously increases the GHRH-stimulated secretion of hGH by the somatotrophe cells in the anterior pituitary. The current understanding of Alpha-GPC's actions in the brain is that it increases hGH secretion in the pituitary by two (2) separate but interacting neuro-endocrine mechanisms; these are:
1. Modulatory - increasing cholinergic tone lending to decreased levels of somatostatin (produced by the hypothalamus), as a result of the administration of Alpha-GPC;
2. Regulatory - stimulation of hGH synthesis resulting from 'up regulation' of Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone/Factor (GHRH/GHRF) in conjunction with receptor-linked stimulation of the adenylate cyclase (cAMP)-Protein kinase C (PKC)-inositol triphosphate (IP3) intracellular control mechanisms regulating hGH synthesis at the genomic level and its subsequent secretion by the anterior pituitary.
Alpha-GPC has been administered to over three thousand (3,000) patients and volunteers in clinical trials and studies that have been published in the peer-reviewed literature. Minor, transient side effects have been reported to occur at a one percent (1%) frequency; these side effects, for orally administered Alpha-GPC, included diarrhea, dizziness, gastralgis, heartburn, insomnia, restlessness and skin rashes, which resolved when the amount of Alpha-GPC administered was either decreased or eliminated.
Alpha-GPC in the mental recovery of transient ischemic attacks or acute stroke.
Institute of Internal Medicine and Geriatrics, University of Palermo, Italy.
The clinical efficacy and the tolerability of alpha-glycerophosphocholine (alpha-GPC), a drug able to provide high levels of choline for the nervous cells of the brain and to protect their cell walls, have been tested in a clinical open multicenter trial on 2044 patients suffering from recent stroke or transient ischemic attacks. alpha-GPC was administered after the attack at the daily dose of 1000 mg im for 28 days and orally at the dose of 400 mg tid during the following 5 months after the first phase. The evaluation of the efficacy on the psychic recovery was done by the Mathew Scale (MS) during the period of im drug administration, and using the Mini Mental State Test (MMST), the Crichton Rating Scale (CRS), and the Global Deterioration Scale (GDS) during the following period of oral administration. The MS mean increased 15.9 points in 28 days in a statistically significant way (p < 0.001) from 58.7 to 74.6. At the end of the 5 month oral administration, the CRS mean significantly decreased 4.3 points, from 20.2 to 15.9 (p < 0.001); the MMST mean significantly increased (p < 0.001) from 21 to 24.3 at the end of the trial, reaching the "normality" score at the 3rd month assessment. The GDS score at the end of the trial corresponded to "no cognitive decline" or "forgetfulness" in 71% of the patients. Adverse events were complained of by 44 patients (2.14%); in 14 (0.7%) the investigator preferred to discontinue therapy. The most frequent complaints were heartburn (0.7%), nausea-vomit (0.5%), insomnia-excitation (0.4%), and headache (0.2%). The trial confirms the therapeutic role of alpha-GPC on the cognitive recovery of patients with acute stroke or TIA, and the low percentage of adverse events confirms its excellent tolerability.(ann ny acad sci 1994 June)
|
| |
| References: |
 |
De Jesus Moreno Moreno M (January 2003). "Cognitive improvement in mild to moderate Alzheimer's dementia after treatment with the acetylcholine precursor choline alfoscerate: a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial". Clin Ther 25 (1): 178–93. doi:10.1016/S0149-2918(03)90023-3. PMID 12637119. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0149291803900233. |
|
|
 |
Parnetti, Lucilla; et al. (2007). "Cholinergic precursors in the treatment of cognitive impairment of vascular origin: Ineffective approaches or need for re-evaluation?". Journal of the Neurological Sciences 257: 266. PMID 17331541. |
|
|
 |
Barbagallo Sangiorgi G, et al. "Alpha-Glycerophosphocholine in the mental recovery of cerebral ischemic attacks." An Italian multicenter clinical trial. Ann NY Acad Sci 1994; 717:253-69. | |
| | |
|