|
hc8meifmdc|20005939267D|healthm_live|health_library|health_library_details|0xfdff8dbd010000003301000001000500
| Overview |
Ribose is a special carbohydrate that is used in the body for energy production in the cells as it plays a critical role in the production of ATP. ATP is what provides the energy needed for short burst of power movements during physical activity. Ribose is used to help to strengthen muscles, including the heart, enhancing athletic performance, recovery from physical activity, and to increase energy levels. D-Ribose is a nutritional supplement that has been around for a long time but has become one of the one of the most sought supplements of late after new research on this very promising product. An energizing nutrient added to EMV, ribose is a carbohydrate that when combined with other components increases production and storage of cell energy.
What is D-Ribose? |
 |
| |
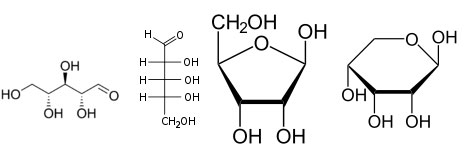
Ribose is an organic compound with formula C5H10O5; specifically, a monosaccharide (simple sugar) with linear form H-(C=O)-(CHOH) 4-H, which has all the hydroxyl groups on the same side in the Fischer projection. The term may refer to any of two enantiomers: almost always to D-ribose, which occurs widely in nature and is discussed here; or to its synthetic mirror image L-ribose, which is not found in nature and is of limited interest.
D-ribose was first reported in 1891 by Emil Fischer. It is a C'-2 carbon enantiomer of the sugar D-arabinose (both isomers of which are named for their source, gum arabic) and ribose itself is named as a transposition of the name of arabinose (http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/sce.3730420523/pdf). Ribose comprises the backbone of RNA, a biopolymer that is the basis of genetic transcription. It is related to deoxyribose, as found in DNA. Once phosphorylated, ribose can become a subunit of ATP, NADH, and several other compounds that are critical to metabolism.
Difference between ribose and d-ribose?
Ribose and d-ribose are almost the same. The only difference is that d-ribose is a more bioavailable form of ribose and is considered to be absorbed more efficiently and completely in the body.
D-ribose has a sweet taste. The supplement is easily soluble in hot and cold water and can be mixed with other drinks or foods without losing its effectiveness. The body uses d-ribose specifically and only for cellular energy. And there are little or no evidence that this substance is toxic in excess, like other sugars.
One should be aware that taking d-ribose on an empty stomach may cause blood-sugar swings, and it is advised to consult a healthcare practitioner prior to starting the use of this supplement if there is proneness to blood-sugar problems.
How is it Made?
D-ribose is a pentose (five-carbon sugar) mainly found in ribonucleic acid (RNA). It is very essential for life, although the substance is a non-essential nutrient. It is made naturally in the body from glucose. Glucose can be found in fruit, berries, vegetables, and honey. In glucose-deficient conditions, like starvation, or strenuous exercise, our liver and even kidneys may also synthesize glucose from other compounds to provide a source of d-ribose for the cells.
The potent ingredients of d-ribose play an important role in the stress related control. The substance is easily absorbed with the diet and has a sweet taste.
When the carbonyl is faced by an alcohol in the chain of ribose, a five-member ring called furanose is formed. The ring of d-ribose has four carbons and one oxygen. The full chemical formula for d-ribose is C5H10O5, meaning that there are 5 carbons, 10 hydrogens, and 5 oxygens.
D-ribose can also be produced by fermentation of corn syrup and it can be obtained from some RNA-rich food substances like brewer's yeast.
Where is it Found?
D-ribose can be found in red meat, particularly veal, which contains the highest concentration of this substance. Brewer's yeast is rich in RNA and is also considered to be a rich source of D-ribose. |
| |
|
|
|
|
Benefits / Uses
Ribose powder restores body's core energy and keeps it fully charged all day long. Ribose is produced by the body naturally, though this process is very slow. The d-ribose powder can quickly restore and maintain depleted energy reserves and as a result, the daily intake of this supplemental powder reduces muscle stiffness, soreness and fatigue. Being one of the more popular supplements among endurance athletes, ribose helps athletic performance by supplying cells in the muscle tissue with a continious supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) which is known as a cellular energy.
While ribose powder and capsules are widely popular among bodybuilders and other athletes, clinical research of this compound is still inconclusive. However, several studies of d-ribose powder have demonstrated that this substance does indeed help speed recovery of the heart muscle after a heart attack. It also improves blood flow to the heart in those affected by ischemia. Furthermore, ribose supplementation has also been used to support heart function and improve cardiac tissues after heart surgery and heart attack.
A recent study shows that d-ribose powder may also be helpful in recovery promotion in those with illnesses characterized by the ATP depletion (for instance, fibromyalgia and Huntington’s disease). It is assumed that the effectiveness of this substance may be due to the fact that it is a small molecule and easily crosses the blood brain barrier.
The intake of d-ribose powder seems to be effective to treat myoadenylate deaminase deficiency (MAD), also known as AMP deaminase deficiency, and the symptoms like cramping, pain, and stiffness after exercise in patients with MAD. At least one study shows that the intake of d-ribose before and during workouts can be used to prevent the symptoms.
There is still insufficient evidence that d-ribose can be used to improve the following conditions or symptoms:
Chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS)
Many bodybuilders and athletes reported that the daily use of d-ribose powder might improve energy, sleep and general health state when they experience chronic fatigue syndrome.
Congestive heart failure (CHF)
The daily use of ribose supplementation during 3 weeks demonstrated the improval of heart function and the quality of life in patients with congestive heart failure.
Fibromyalgia
Several studies show that the daily intake of ribose supplements can be effective for energy promotion, sleep and the sense of well-being in patients with fibromyalgia.
Skin and Aging
A recent study demonstrates that d-ribose can act as a regenerative material. When placed on the skin, the substance is can decrease wrinkling and aging signs in patients.
Antioxidant
D-ribose may be effective as an antioxidant in the human body. According to a 2002 research published in the Free Radical Biology Medicine journal, 7 grams before and after physical exercise helps reduce the amount of free radical production.
Supports normal heart function
A significant amount of in vitro, animal and human research suggests benefits of ribose on heart function. Studies have shown that ribose supplementation can enhance cardiac energy levels and support cardiovascular metabolism. Ribose has been shown in clinical trials to enhance the recovery of heart muscle ATP levels and improve myocardial function following exercise.
Studies suggest that ribose supplementation can increase the tolerability of the cardiovascular system to exercise-induced fatigue. In one study, twenty men underwent treadmill exercise tests on two consecutive days to confirm the onset of fatigue secondary to exercise. The participants were then randomized to the treatment group or a placebo group. The groups received either four doses of 15 grams of D-ribose (60 grams/day total) or the same amount of placebo each day. After three days of treatment, another treadmill test was performed. The time it took to reach the specified level of fatigue was significantly greater in the ribose group than in the placebo group.
Another study investigated the ability of ribose to support healthy heart function and quality of life. In a randomized, crossover design study, fifteen individuals were given 5 grams three times a day of either D-ribose or placebo. Each treatment period lasted three weeks. In patients receiving ribose, echocardiography demonstrated enhancement of heart function, reflecting a “more efficient relaxation phase of the heartâ€. Participants also had a significant improvement in their subjective quality of life scores compared to placebo.
Scientists suggest that suboptimal heart function is a result of the heart requiring more energy to function properly. Ribose supports the heart’s enhanced energy requirements, promoting optimal heart function. It does so by enhancing the stores of high-energy phosphates in heart tissue. These intermediates are necessary for the production and resynthesis of ATP. A double-blind crossover study in which 12 individuals were randomized to receive either ribose or dextrose (both administered as 5 grams three times daily for three weeks, followed by a 1-week washout period and crossover of treatments for three additional weeks) suggested significant enhancements in normal cardiac function during the period of ribose supplementation.
Perhaps one of the more useful illustrations of the potential for ribose to support heart function comes from a study in which 20 rats received a continuous infusion of ribose for 24 hours (control rats received an infusion of saline). The hearts were then explanted (as they would be for heart transplants) and placed in preservation solution that was enriched with ribose for 4 hours. ATP levels were measured from tissue biopsies and revealed that 10 of the ribose-treated hearts had ATP levels higher than 12.3 micromoles per gram whereas saline-treated hearts (controls) had lower ATP levels, with 20% showing levels below 10 micromoles per gram of tissue. This provides support for the hypothesis that ribose may enhance the preservation of ATP levels in cardiac tissue, promoting normal heart function.
Further animal studies have shown that ribose significantly enhances heart function after experimentally induced cardiac depression. Rats were injected with isoproterenol (a drug that stimulates sympathetic nervous system function) and had their abdominal aorta constricted to induce depression of heart function and reduce cardiac ATP levels. The decrease in ATP was primarily responsible for the depression of heart function. Continuous infusion of ribose for 24 hours replenished ATP concentrations to normal levels and normalized heart function in these animals.
Ribose may strengthen and support the body’s crucial antioxidant defenses. Ribose may support the body’s innate antioxidant mechanisms while promoting an antioxidant effect of its own. Intense exercise and other strenuous activity can induce the production of free radicals. Preliminary studies suggest that ribose can attenuate some of the effects of oxidation seen after performance of intensive exercise.
One small human study indicated that ribose administered at a dose of seven grams before and after a bout of cycling exercise may reduce free radical production. Seven volunteers ingested either ribose or placebo both before and after intense exercise. Markers of lipid peroxidation, including malondialdehyde, significantly decreased in the ribose-supplemented group, while increasing in the control group. The results of this study indicate a possible effect of ribose in supporting antioxidant activity.
Supports healthy energy levels in heart and muscle tissue
After bouts of intense exercise, ATP levels have been shown to decrease by an average of 15 to 20%. The amount of ATP stored in the muscle is limited and so the body must have the potential to rebuild ATP stores. ATP is the fuel necessary for the integrity and function of a cell. In addition, several studies have found correlations between ATP content and heart function.1 Research that was also alluded to above suggests that ribose stimulates ATP synthesis and supports heart and muscle function by enhancing ATP levels in cardiac and muscle tissue. D-ribose is an essential building block for the synthesis of ATP through the pentose phosphate pathway.
The results of ribose supplementation enhancing ATP levels in muscle are evidenced by studies suggesting beneficial effects on anaerobic performance. In a randomized, placebo-controlled crossover study assessing the effects of acute ribose supplementation, participants receiving the ribose supplement had increases in mean power (a measure of average overall muscular strength output during the sprint) and peak power (a measure of the highest muscular strength output during the sprint) when undergoing a series of cycle sprints. While this effect was not noted in all of the six short cycling sprints that the participants underwent, the study does illustrate the potential benefits of ribose on ATP production and, secondarily, on enhancing exercise performance.
A second placebo-controlled trial investigated the effects of four weeks of ribose-supplementation (10 grams /day) on male bodybuilders. Of the 20 participants who were recruited, twelve completed the study. Each subject participated in a heavy-resistance training program designed to increase skeletal muscle mass. The effects of ribose on body composition (body weight, body fat, lean body mass, fat mass, and bone mineral content) were also assessed. The results suggested that ribose increased total work capacity and bench press strength compared to placebo, without altering body composition.
Supports energy recovery after exercise
Animal studies have suggested that the administration of ribose after exercise increases the rate of adenine salvage by five to seven-fold in muscle tissue, supporting energy recovery after exercise. When ATP is utilized by muscle tissue, the degradation products include adenine nucleotides (Adenine is one of two purine bases that is a component of DNA). Adenine is recycled to synthesize DNA, and the salvage of adenine within the muscle tissue is crucial to energy recovery. Studies have shown that the presence of adequate ribose concentrations is the rate-limiting step in the purine salvage pathway. Therefore, increased adenine salvage could potentially help in the recovery and regeneration of ATP after intense bouts of activity.
A study investigated the effect of oral intake of ribose on the synthesis of AMP, a precursor to ATP. Participants performed intense cycle training for seven days. They then received either ribose (at a concentration of 200 mg/kg body weight, which is equivalent to 14 grams per day for an average 70 kilogram male) or placebo three times a day for the following three days. Exercise tests were performed again on day 4. Muscle biopsy samples were taken before the first training session, immediately after, and again five hours, 24 hours, and 72 hours after the last training session. No differences were seen in exercise performance between the groups. The intense exercise caused the ATP levels in muscle to decrease in both groups. However, at 72 hours post-exercise, the ribose group exhibited a much higher ATP level than the placebo group. The muscle levels of critical building blocks for ATP, including total adenine nucleotides (TAN) and inosine 5’-monophosphate (IMP), were also significantly higher in the ribose group compared to the placebo group at 24 hours after exercise. Ribose-supplementation was shown to enhance the resynthesis of ATP after intense exercise.
Ribose and in weight loss
D ribose is a natural anti-stress relief ingredient that is used to control stress-related eating and drinking, thus adding the value of being non-sedating with potential anti-depressant properties. At least one study shows that d ribose is beneficial for weight loss because it can help shorten recovery time between workouts, which allows people on weight loss programs to work out more often and more effectively. Although ribose is essential for energy production, it is not recognized as a fuel by the body, thus this substance is actually of no caloric value to humans.
D ribose powder and ester creatine
By far, ester creatine and d ribose powder are among the best discoveries that has ever been made in the world of bodybuilding and fitness. Creatine is made in the body from such amino acids as glycine and arginine. It is also derived from foods, especially meat and animal products. While in the body creatine ester is changed into a molecule that is called phosphocreatine. This molecule serves as a storage reservoir for regenerating ATP. This function is widely supported by d ribose powder and maintains cellular energy (ATP) at the highest level. In common words, ATP is the chemical source of energy for muscle tissues and quick energy. Several studies have shown that the combination of d ribose powder and ester creatine can increase the performance of athletes involved in strenuous training like sprinting and weight lifting.
Creatine ester and d ribose powder supplementation combined with physical workouts can cause dramatic improvements in muscle size and strength through cell volumization and increased protein synthesis.
Long-term clinical studies have shown that creatine ester and d ribose powder are safe for use by people without medical conditions. However, if you experience any health problems, consult your healthcare practitioner before starting the intake of any supplements containing d ribose or creatine.
D-ribose + r-alpha lipoic acid
R-alpha lipoic acid (R-ALA) is a popular antioxidant that helps protect the body’s cells, including brain and nerve cells. The combination of d-ribose + r-alpha lipoic acid protects from free radicals and toxins. Not only does this mix act as a powerful antioxidant, it also protects the brain cells by binding such metals as iron, copper, and cadmium. There is also evidence that suggests that d-ribose and r-alpha lipoic acid is very helpful for patients suffering from neurological disorders, including Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s, Alzheimer’s, and primary dystonia.
Beta alanine and d-ribose
Beta alanine is one of the natural beta amino acids and is one of the components in natural peptides anserine, carnosine and panthotenic acid. This compound limits carnosine and increases the concentration and the presence of carnosine in different muscle tissues in the body. When taken by athletes and bodybuilders, the combination of beta alanine and d-ribose helps decrease fatigue syndroms and ultimately increases the total energy and muscle performance. Beta alanine and d ribose can also increase energy an average of 45% and activate diverse energy systems within the body. According to at least one study, the affect from the beta alanine and d-ribose intake can be felt in an average of 12 days.
Dosage
One teaspoon equals to 5 grams of d-ribose powder. As 500 milligrams is half a gram, it equals to approximately 1/10th of a teaspoon. Four ounces (4 oz) approximately equals to 113,4 grams or 113398 milligrams of pure ribose powder.
During the loading phase to make your muscles stronger, you should take three grams of d-ribose 3 - 4 times a day. During the maintenance phase, take 3 - 6 grams of this substance a day.
Bodybuilders recommend starting with one full scoop (around 5 grams) three times a day. After 1 month, the dose of d-ribose can be decreased to the minimum dosage that maintains the same benefit (that is, 1 scoop twice a day).
Studies showed that for maximum effect, the best time to take d ribose is before and during exercise, when the body responses actively to the changes in the cells.
Physicians recommend to use d-ribose for a little bit of extra energy. For these purposes, you should generally need to take only one or two capsules or one half teaspoon of powdered d-ribose a day orally. To offset the blood glucose-lowering effect, the substance is normally mixed into hot or cold meals or at least juice, milk, or fruit. Your dose will be near a gram and a half of d-ribose and this is a nice dosage for a relatively healthy person.
However, if you are suffering from any kind of energy deficit disorder, you may want to take significantly larger doses of d-ribose or take it in some other ways to maximize its energy-boosting benefits without having to increase the dosage: |
| |
 |
Pour the d-ribose powder directly under your tongue and leave it in your mouth for several minutes. This allows the body to absorb much of d-ribose directly into the bloodstream through the rich network of veins under your tongue. |
|
|
 |
Take d-ribose powder along with synergistic nutrients such as B-vitamins. This will maximize the energy-boosting benefits of d-ribose and will significantly effect its effect throughout the day. You can also take d-ribose with other substances such as magnesium (200mg), tyrosine (500mg), malic acid (900mg), selenium (200mcg), iodine (200mcg), and vitamin C (500mg). |
|
|
 |
A very powerful way to maximize your d-ribose energy effect is to take it with an immune system booster, e.g. beta-glucan. This little-known secret is used by numerous bodybuilders and athletes suffering from severe chronic fatigue and who used this combination to quickly recover from a debilitating chronic fatigue. Taken together, the synergy between these two supplements appears to double the individual benefits of each d-ribose and beta-glucan. The energy can be usually restored within just a couple of hours. When taken for several days in a row, the energy- and mental-boosting effects of this combination can last for several days to several weeks afterwards. | |
| |
|
Doses for fibromyalgia:
The first thing you should do is to figure out the root cause of fibromyalgia (muscle pain, in plain words). Usually, the underlying cause of this condition is candida overgrowth or adrenal fatigue. The use of d-ribose powder has evidence of its effectiveness for fybromyalgia, though its benefits are short term. Published in 2006 in the Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine a pilot study called The Use of D-Ribose in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome and Fibromyalgia explored the use of D-ribose to decrease the debilitating symptoms of both fibromyalgia (FMS) and chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS). Most frequently, these syndromes are associated with impaired cellular energy metabolism. In this pilot study, the subjects were given a dosage of 5 grams three times a day for a total amount of 280 grams. The scientists made the following conclusion based on the results of their research:
D-ribose was well-tolerated and resulted in a significant improvement in all five visual analog scale categories: energy, mental clarity, sleep, pain intensity, and general well-being. Approximately 66% of the subjects felt dramatic improvement when taking d-ribose, with an average increase in energy in 45% and an average improvement in overall well-being of 30%.
How long does it take D-Ribose to take effect?
Though there is still little evidence on the effectiveness of d-ribose, about 60% of the subject who took part in 2009 research, felt a boost in energy, as well as the ability to train harder and longer.
Usually, it takes about 3 to 4 days to feel the effect; however, the research suggests that the benefits from the d-ribose intake will be felt if individuals exercises hard enough to deplete adenine nucleotide pools. You might not feel it, but d ribose works to enhance the body’s energy and cells recovery.
The biochemistry about this process is quite clear. In all strenuous physical exercise adenine nucleotides decrease their amount under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. If bodybuilders or athletes train hard enough to lower the cellular energy charge, then d ribose will assist in recovery. It’s can be compared with a rapid recharge on a rechargeable battery.
Commonly Asked Questions/Doubts
Can ribose powder be used to sweeten iced tea?
Ribose powder is a 5-carbon sugar that is essential for the synthesis of ATP, the cells energy molecule. The supplement helps protect tissues from energy deprivation, and stimulates recovery following a hypoxic or ischemic event. Healthy people the intake of pure d ribose powder may translate to more energy and less fatigue, greater exercise performance (in the long term), and faster recovery from exercise or overexertion. As ribose powder has a sweet taste and is easily soluble both in hot and cold water, it can be added to drinks, including iced tea. Thus you get a powerful energy-boosting drink that tastes greatly.
Can d-ribose be added in fruit juice?
Yes, d-ribose can be added in fruit juice. The supplement is easily soluble in juice and can be used even with plain water, although it is not recommended to use d-ribose on empty stomach because it might raise blood sugar.
Can you put d-ribose in coffee?
The combination of d-ribose with coffee is a very good idea. Coffee (and its main ingredient caffeine) acts as a stimulant. However, besides its beneficial effects, coffee produces several unpleasant side effects such as insomnia, an increased heart rate, anxiety, headaches, and a potential crash state following its metabolism. Several researchers have proposed mechanisms responsible for caffeine’s interactions. The results of their investigations have produced no positive consensus; however d-ribose, which is an important pent pentose carbohydrate in the energy molecule of ATP, may become a good solution to this problem. Potentially, d-ribose may help maintain or lower extra-cellular adenosine concentrations and lessen fatigue and depression. Every cell requires energy to maintain its integrity and function. The mix of d-ribose powder with caffeine might help in the potential intracellular energy demand and lessen the unpleasant side effects of coffee intake, and at the same time preserve the desired benefits of this stimulant.
Possible Side-Effects / Precautions / Possible Interactions:
When taken at doses no more than 10 grams a day, d-ribose is considered to be safe. D-Ribose may cause such unwanted gastrointestinal conditions as diarrhea, and a decrease in blood glucose levels, although it is not known whether symptoms of hypoglycemia might result.
Can ribose cause stomach upset?
When taken in smaller doses (up to 20 grams a day), ribose powder doesn’t cause stomach upset, however at larger doses people may experience gastrointestinal symptoms like diarrhea, nausea and stomach upset.
Can ribose make you have nausea?
At extremely large doses (up to 60 grams a day), ribose powder may make you have nausea, although when you take the supplement with the interval of at least 30 minutes, your body may be able to metabolise ribose just fine.
Can d-ribose be taken by diabetics?
D-ribose is a sugar produced by the body. This makes this supplement contraindicated for those suffering from diabetes or low blood sugar (hypoglycemia).
A small amount of d ribose powder, pill, or liquid may not make much of a difference on blood sugar levels, however diabetics should be very cautious with larger doses. As an alternative recommendation, diabetics who take d-ribose supplementation should take a 5 to 10 minute walk after consuming the supplement. This will minimize any potential rise in blood sugar.
In any case, if you have diabetes, d-ribose must be taken under your physician’s supervision, and your blood glucose levels should be closely monitored, as well as the doctor should reconsider the dosages of anti-diabetic medications, if necessary.
Can d-ribose raise your insulin levels?
When taken in doses larger than 10 grams a day, d-ribose can mildly lower blood glucose levels. That is why, insulin-dependent diabetics should check with their healthcare provider before starting their intake of d-ribose supplements. For more information, please refer to the section “Can d-ribose be taken by diabeticsâ€.
Is d-ribose safe with coffee?
Yes, it is not only safe to put d-ribose in coffee, but may bring positive effect to your well-being. D-ribose neutralizes some negative effects of caffeine and adds extra boost to your cellular energy. For more information, see the section above “Can you put d-ribose in coffeeâ€.
Is it safe to take ribose while nursing?
Although there are no known contraindications of the ribose therapy, it is not recommended to use this supplement for pregnant women, nursing mothers, and young children. Before starting your intake of d-ribose supplements, it is highly recommended that you consult your doctor first.
Can one take d-ribose when pregnant?
Although there are no sufficient studies to demonstrate that d-ribose is either safe or not, it is not recommended to use this supplement when pregnant.
Can d-ribose be taken while breast feeding?
No sufficient data is available to prove the safety of d-ribose, therefore you should avoid taking this powder while breast feeding.
Can d-ribose cause creatine build up in the body?
The reason why d-ribose and creatine are so closely related is the way in which they function. D-ribose supplements work synergistically with and enhance the benefits of creatine. If you remember, simple sugars raise the insulin level in the blood and therefore facilitate the absorption of protein and creatin.
When you train intensely, your skeletal muscle energy levels experience a significant decrease. In fact, it can take 3 or even more days for these energy levels to recover. However, recent studies demonstrate that pure d ribose powder hastens energy recovery in all types of skeletal muscles. What this means for your body? - This means that you will be able to work out longer and build muscles faster. And all this happens because your body will recover quicker from workouts and you will have more energy to exercise even more.
What medications react with Ribose?
If you have diabetes and use medications to treat this condition, remember that they can interact with d-ribose and cause an unsafe drop in blood sugar. If d-ribose is recommended by your physician, most likely your dosage of diabetes medications will need to be modified.
Alcohol can also interact with d-ribose. When combined, alcohol and d-ribose may lead to a significant drop in blood sugar.
Ribose interacts with other medications and drugs such as aspirin, inderal, trilisate, and disalcid.
Should you take angioprim before or after d-ribose?
EDTA Disodium, also known as Angioprim, is used to assist with unwanted arterial plaque, heavy metals and decalcifying of internal organs like pancreas, kidneys, and liver.
The first dose of angioprim should be taken before d-ribose in about 30 minutes before your breakfast. Then it is recommended to have your EDTA dose 2 hours after lunch and at least one hour before dinner. Remember, that you should avoid taking d-ribose on empty stomach, thus angioprim will be taken before your d-ribose dose. |
| |
| Research Studies / References |
 |
Pliml, W., von Arnim, T., Stablein, A., Hofmann, H., Zimmer, H., Erdmann, E. Effects of ribose on exercise-induced ischaemia in stable coronary artery disease. The Lancet. 1992;340:507-510. |
|
|
 |
Omran, H., Illien, S., MacCarter, D., St. Cyr, J.A., Luderitz, B. D-Ribose improves diastolic function and quality of life in congestive heart failure patients: a prospective feasibility study. The European Journal of Heart Failure. 2003;5:615-619. |
|
|
 |
Illien, S., Omran, H., MacCarter, D., St. Cyr, J.A. Ribose improves myocardial function in congestive heart failure. FASEB Journal 2001;15(5): A1142 |
|
|
 |
Muller C., Zimmer H., Gross M., Gresser U., Brotsack I., Wehling M., Pliml W. Effect of ribose on cardiac adenine nucleotides in a donor model for heart transplantation. Eur J Med Res. 1998 Dec 16;3(12):554-8. |
|
|
 |
Zimmer H.G. Normalization of depressed heart function in rats by ribose. Science. 1983 Apr 1;220(4592):81-2. |
|
|
 |
Seifert, J.G., Subudhi, A., Fu, M., Riska, J.J. The effects of ribose ingestion on indices of free radical production during hypoxic exercise. Free Rad Biol Med 2002; 33(Suppl 1) S269. |
|
|
 |
Zarzeczny, R., Brault, J.J., Abraham, K.A., Hancock, C.R., Terjung, R. Influence of ribose on adenine salvage after intense muscle contractions. J Applied Physiology. 2001;91:1775-1781. |
|
|
 |
Berardi J.M., Ziegenfuss T.N. Effects of ribose supplementation on repeated sprint performance in men. J Strength Cond Res. 2003 Feb;17(1):47-52. |
|
|
 |
Van Gammeren, D.V., Falk, D., Antonio, J. The effects of four weeks of ribose supplementation on body composition and exercise performance in healthy, young, male recreational bodybuilders: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Current Ther Research. 2002;63(8):486-495. |
|
|
 |
Hellsten, Y., Skadhauge, L., Bangsbo, J. Effect of ribose supplementation on resynthesis of adenine nucleotides after intense intermittent training in humans. American Journal of Physiology - Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology. 2004;286:R182-R188. | |
| |
|