|
hc8meifmdc|20005939267D|healthm_live|health_library|health_library_details|0xfdffb9bd010000009901000001000e00
| Overview |
be at risk of ornithine deficiency. In fact, those diets that lack in meat or dairy products, without supplementation, can easily lead to a deficiency in several amino acids. Pregnant women are also at risk for being deficient, largely in part because of the general need for more food during the growth of the fetus. Lastly, people that suffer from malnutrition will obviously be at risk for nutrient and mineral deficiencies.
Also, since arginine is required to create ornithine in the body, then a deficiency in arginine can lead to an ornithine deficiency. This is one of the reasons why supplementation of these aminos, and others, might be important for you. Lacking in any amino acid or in protein can result in muscle catabolism, lack of growth tissue inside the body, and several side effects, such as fatigue.
Ornithine is alpha-gamma-diaminovaleric acid, synthesized from arginine. Closely related in the formation of urea, in Krebs Hensleit urea cycle, ornithine takes part in the synthesis of citrulline where it reacts with carbamyl phosphate to form citrulline. Ornithine is a non-essential amino acid and is manufactured by the body. The amino acid, arginine, is metabolized during urea production and is required by the body as it acts as a precursor of citrulline, proline and glutamic acid. Ornithine may take part in the synthesis of proline and glutamic acid.
Ornithine is often combined with arginine and marketed to body builders as a muscle-building supplement. Laboratory studies have shown that ornithine increases both insulin and growth hormone levels, which are needed to build and maintain muscle during intensive physical training. It helps build muscle and reduce body fat, especially when combined with the amino acids arginine and carnitine.
Ornithine is also marketed as an anti-aging drug since it is believed to help combat the muscle loss. As the body ages, it is less efficient at synthesizing proteins and can't regenerate muscle tissue as quickly-strength and muscularity begin to decline. By helping to elevate growth hormone levels, ornithine may help speed the production of muscle tissue and offset the effects of aging. Although both arginine and ornithine help protect and build muscle mass, ornithine is generally thought to be twice as effective at stimulating growth hormone production as arginine, so a combination supplement is not necessary if one wishes to use ornithine for this purpose.
In clinical studies done on people hospitalized for surgery, generalized infections, cancer, trauma, or burns, supplementation with ornithine alpha-ketoglutarate (OKG) has been reported to produce several beneficial effects including increased ability to heal, improvement in appetite, weight gain, and quality of life compared with those who did not supplement with OKG. Preliminary trials using ornithine aspartate, another derivative of ornithine, has shown to help people with brain abnormalities (hepatic encephalopathy) due to liver cirrhosis. Those taking the ornithine had significant improvements in liver function and blood tests compared with those who did not take ornithine. Other studies also indicate that ornithine can help those who have suffered from severe burns. In a clinical trial, burn patients who took 10-30 grams of ornithine alpha-ketoglutarate per day experienced an improved healing and shorter hospital stays.
What is Ornithine?
|
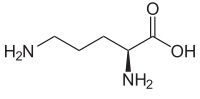 |
L-Ornithine
(+)-(S)-2,5-Diaminovaleric acid |
| |
L-Ornithine, a free-form crystalline amino acid, is a precursor of arginine, which is necessary for the synthesis of creatine, an important energy provider for muscles. In addition, L-Ornithine is a key compound in the urea cycle, one of the body's main processes for eliminating ammonia.
Where is it Found?
Body can manufacture ornithine by itself but is found in abundant in protein rich food, like meat, fish, diary, and eggs. If you are a vegetarian or a vegan, you might be at risk of ornithine deficiency. In fact, those diets that lack in meat or dairy products, without supplementation, can easily lead to a deficiency in several amino acids. Pregnant women are also at risk for being deficient, largely in part because of the general need for more food during the growth of the fetus. Also, people who suffer from malnutrition will obviously be at risk for nutrient and mineral deficiencies.
Since arginine is required to create ornithine in the body, thus a deficiency in arginine can lead to an ornithine deficiency. Lacking in any amino acid or in protein can result in muscle catabolism, lack of growth tissue inside the body, and several side-effects, such as fatigue.
Benefits / Uses
Ornithine is important since it induce the release of growth hormone in the body, which in turn aids fat metabolism. It is further required for a properly functioning immune system and liver and assists in ammonia detoxification and liver rejuvenation. It is also useful in healing and repairing skin and tissue and is found in both these body parts. Ornithine helps remove toxic ammonia from the liver, and may reduce the effects of cirrhosis of the liver and disorders associated with liver malfunction.
Ornithine may also help combat the muscle loss that is a normal part of the aging process. As the body ages, it is less efficient at synthesizing proteins and can't regenerate muscle tissue as quickly-strength and muscularity begin to decline. By helping to elevate growth hormone levels, ornithine may help speed the production of muscle tissue and offset the effects of aging. Ornithine is also needed for the formation of citrulline, proline, and glutamic acid, the three amino acids which help supply energy to every cell in the body.
It also helps to fasten the process of healing in cases of burns, trauma, improvement in appetite, weight gain and improvement in quality of life. People recovering after surgery and athletes may benefit from this nutrient.
Deficiency Symptoms of Ornithine
Since the body can produce ornithine, a deficiency of this non-essential amino acid is rare. Few people are really deficient in ornithine, unless they are extremely malnourished or have a disorder that disrupts the citric acid cycle.
Dosage
In human research involving ornithine, several grams are typically used per day, sometimes combined with arginine. For those who supplement with ornithine, 5-10 grams is a typical daily dosage (sometime combined with arginine). However, most healthy people do not need to take ornithine supplements.
Possible Side-Effects / Precautions / Possible Interactions
There are no reported side effects from the use of ornithine, but children, pregnant or nursing mothers, or anybody suffering from schizophrenia should NOT take L-ornithine.
Gastrointestinal distress has been reported with intakes over 10 grams of ornithine per day.
Research Studies / References
|
 |
Weast, Robert C., ed. (1981), CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (62nd ed.), Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, p. C-408, ISBN 0-8493-0462-8. |
|
|
 |
Ornithine Biosynthesis, School of Biological and Chemical Sciences, Queen Mary, University of London, http://www.chem.qmul.ac.uk/iubmb/enzyme/reaction/AminoAcid/Orn.html, retrieved 2007-08-17. | |
| | |
|