|
hc8meifmdc|20005939267D|healthm_live|health_library|health_library_details|0xfdffc5bd010000009901000001001f00
| Overview |
|
Theanine is an amino acid (a building block for proteins) found in green tea.
People use theanine for treating anxiety and high blood pressure, for preventing Alzheimer’s disease, and for making cancer drugs more effective. Theanine has a chemical structure very similar to glutamate, a naturally occurring amino acid in the body that helps transmit nerve impulses in the brain. Some of the effects of theanine appear to be similar to glutamate, and some effects seem to block glutamate.
What is Theanine?
|
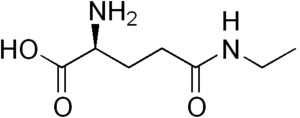 |
| 2-Amino-4-(ethylcarbamoyl)butyric acid |
| |
Theanine is a glutamic acid analog or amino acid derivative commonly found in tea (Camellia sinensis).
Where is it Found?
It is mainly found naturally in tea leaves (Camellia sinesis) and other species of Camellia, as well as edible bay boletes mushrooms (Xerocomus badius).
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| Benefits / Uses |
|
|
 |
Anxiety. Preliminary evidence suggests that taking theanine might make unstressed people feel more tranquil. But theanine doesn’t seem to have this effect on people who are anxious to start with. |
|
|
 |
Preventing dementia including Alzheimer's disease. |
|
|
 |
Treating high blood pressure. |
|
|
 |
Increasing the treatment effects of cancer drugs. | |
| |
L-theanine is involved in the formation of the inhibitory neurotransmitter, gamma amino butyric acid (GABA). GABA influences the levels of two other neurotransmitters, dopamine and serotonin, producing a relaxation effect. GABA serves a sedative function that brings balance to excitability that can lead to restlessness, insomnia, and other disruptive conditions. Theanine also appears to increase levels of dopamine, another brain chemical with mood-enhancing effects, which can reduce blood pressure.
L-theanine is an amino acid that helps promote a mild, restful, relaxed state without diminishing daytime alertness. Stress impairs the immune system, leaving us vulnerable to opportunistic infections, and can cause depression. People under stress can mitigate many of the harmful effects of stress with l-theanine. L-theanine reduces stress and anxiety without the tranquilizing effects found in many other calming supplements.
Theanine has a reputation for promoting mental and physical relaxation, and decreasing stress and anxiety without inducing drowsiness, as measured by increased generation of alpha-waves. L-theanine directly stimulates the production of alpha brain waves. By increasing the brain's output of alpha waves, theanine may control anxiety, increase mental focus, improve concentration, and promote creativity.
Theanine may improve learning ability and sensations of pleasure by affecting dopamine and serotonin neurotransmitters in the brain. L-theanine has a significant effect on the release or reduction of neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin, resulting in improved memory and learning ability. L-theanine may also influence emotions due to its effects on the increased release of dopamine. L-theanine reduces brain serotonin concentration by either curtailing serotonin synthesis or increasing degradation in the brain. Theanine exerts protective effects on the brain by antagonizing glutamate toxicity.
Theanine has been found to be increasingly associated with therapeutic benefits in the areas of cardiovascular health and cancer treatment. Theanine helps to reduce the side effects and enhance the antitumour efficacy of chemotherapy. L-theanine has exhibited anticancer effects and an ability to favorably modulate the activity of some anticancer drugs.
Dosage
An effective dosage of l-theanine is between 50 and 200 mg daily, as required. Individuals with high stress levels may increase their dosage of L-theanine to at least 100 mg, with no more than 600 mg being taken in a six hour period. FDA recommends a maximum dose of 1200 mg daily.
Possible Side-Effects / Precautions / Possible Interactions
Theanine is possibly safe when used once per week for three weeks. It's not known if daily use for longer periods of time is safe.
Special Precautions & Warnings:
Pregnancy and breast-feeding: Not enough is known about the use of theanine during pregnancy and breast-feeding. Stay on the safe side and avoid use.
|
|
|
 |
Medications for high blood pressure (Antihypertensive drugs) interacts with THEANINE
Theanine seems to decrease blood pressure. Taking theanine along with medications for high blood pressure might cause your blood pressure to go too low. |
|
|
 |
Some medications for high blood pressure include captopril (Capoten), enalapril (Vasotec), losartan (Cozaar), valsartan (Diovan), diltiazem (Cardizem), Amlodipine (Norvasc), hydrochlorothiazide (HydroDiuril), furosemide (Lasix), and many others. |
|
|
 |
Stimulant drugs interacts with THEANINE Stimulant drugs speed up the nervous system. By speeding up the nervous system stimulant medications can make you feel jittery and speed up your heartbeat. Theanine might work to slow down the nervous system. Taking theanine along with stimulant medications might decrease the effectiveness of stimulant medications. Some stimulant drugs include diethylpropion (Tenuate), epinephrine, phentermine (Ionamin), pseudoephedrine (Sudafed), and many others. | |
| |
| Research Studies / References |
|
|
 |
Casimir J, Jadot J, Renard M (1960). "[Separation and characterization of N-ethyl-gamma-glutamine from Xerocomus badius.]". Biochim Biophys Acta 39: 462-8. doi:10.1016/0006-3002(60)90199-2. |
|
|
 |
Yokogoshi H, Kobayashi M, Mochizuki M, Terashima T (1998). "Effect of theanine, r-glutamylethylamide, on brain monoamines and striatal dopamine release in conscious rats". Neurochem Res 23 (5): 667-73. |
|
|
 |
"FDA confirms GRAS status of Suntheanine". NutraIngredients-USA.com. March 22, 2007. http://www.nutraingredients-usa.com/Industry/FDA-confirms-GRAS-status-of-Suntheanine. |
|
|
 |
Perrini, Carolyn. "L-Theanine: How a Unique Anxiety Reducer and Mood Enhancer Increases Alpha Waves and Alertness". Okinawa Tea Company. http://www.okinawateacompany.com/html/pdf/mood_3.pdf. |
|
|
 |
Gomez-Ramirez M; Higgins, BA; Rycroft, JA; Owen, GN; Mahoney, J; Shpaner, M; Foxe, JJ (2007). "The Deployment of Intersensory Selective Attention: A High-density Electrical Mapping Study of the Effects of Theanine". Clin Neuropharmacol 30 (1): 25-38. doi:10.1097/01.WNF.0000240940.13876.17. |
|
|
 |
Kimura K, Ozeki M, Juneja L, Ohira H (2007). "L-Theanine reduces psychological and physiological stress responses". Biol Psychol 74 (1): 39-45. doi:10.1016/j.biopsycho.2006.06.006. |
|
|
 |
Haskell CF, Kennedy DO, Milne AL, Wesnes KA, Scholey AB (2008). "The effects of l-theanine, caffeine and their combination on cognition and mood". Biol Psychol 77 (2): 113-22.. |
|
|
 |
Kakuda T, Nozawa A, Sugimoto A, Niino H. Inhibition by theanine of binding of [3H] AMPA, [3H] kainate, and [3H]MDL 105,519 to glutamate receptors. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2002;66(12):2683-6. | |
| | |
|